Thyristor Control of 3-Phase Induction Motors | Electrical Engineering
A square-wave inverter power circuit is illustrated in Fig. 3.38. The three-phase ac supply is converted into dc by a controlled rectifier. The output of the rectifier is supplied to the filter
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
The use of an inverter to adjust the speed and acceleration of an AC motor increases the range of applications of the motor compared with a motor that operates at a constant speed. The speed
Get a quote
How an Inverter Drive Works and Controls the Speed of an AC Induction Motor
An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected
Get a quote
High frequency effects in inverter-fed AC electric machinery
"Steep voltage pulses" means, that the wave propagation time between inverter and motor on the motor cable is in THE SAME ORDER OF MAGNITUDE as the time for voltage build up.
Get a quote
FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND EVERYTHING ABOUT THEM
All of our inverters offer a change of frequency from 0 to 650 Hz. This is considerably more than the permitted speed range for induction electric motors. Consequently, it is possible to regulate
Get a quote
How an Inverter Drive Works and Controls the Speed of an AC
An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected
Get a quote
CSM_Inverter_Selection_TG_E_2_1
load connected to a motor has kinetic energy when rotating, and potential energy when it is located in a high position. When the motor decelerates, or when the load descends, the
Get a quote
What is AC Frequency Inverter
The AC frequency inverter (VFD) is a motor drive, intended for electromechanical drive systems, that regulates the speed and torque of AC motors by varying the motor input
Get a quote
What Makes Three-Phase Motors Better for
4 days ago· The differences between single-phase and three-phase AC induction motors don''t stop with the input power supply. There are a few things you
Get a quote
Guide to Frequency Inverters: Optimizing Motor
Frequency inverters, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), are essential components in modern motor control systems. These
Get a quote
How Does a Frequency Inverter Work?
Frequency inverters can be used in home appliances. Among the home appliances that use a frequency inverter are not only motors (e.g., air conditioners, etc.) but
Get a quote
Guide to Frequency Inverters: Optimizing Motor Performance,
Frequency inverters, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), are essential components in modern motor control systems. These devices convert fixed
Get a quote
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
The use of an inverter to adjust the speed and acceleration of an AC motor increases the range of applications of the motor compared with a motor that operates at a constant speed. The speed
Get a quote
AKX00057-1
The rotation speed, or RPM, of a three-phase AC induction motor is represented by the following equation, which indicates that the RPM is inversely proportional to the number of
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
By changing a parameter or using the inputs of an inverter you are able to change the direction of motor rotation. This is particularly good in applications that may need to travel
Get a quote
Induction motors fed by PWM frequency inverters
The analysis of the formula above shows that the mechanical speed of an induction motor is a function of three parameters. Thus the change of any of those parameters will cause the motor
Get a quote
High-Frequency Bonding for Inverter-Driven Motors and
To facilitate the flow of high-frequency currents and optimize the performance of inverter-driven motor systems, major motor and drive manufacturers recommend bonding all motors, drives,
Get a quote
Induction Motor
Variable Frequency Drives Induction and synchronous motors are designed for a specific voltage per frequency ratio (V /Hz). Voltage is the supply voltage to the motor, and frequency is the
Get a quote
Fed Induction Motor
However, recently, variable speed drives have been made possible by power electronic converters such as inverter, so induction motors are widely used in many applications
Get a quote
Analysis of the Asynchronous Motor Controlled by Frequency
In the mechanism of drive of asynchronous motors, the transient stage is taken into consideration when the change of state is developed by increase or variation of speed where there are
Get a quote
Analysis of Inverter Drive Working System as 3-Phase AC
With a variable speed drive inverter supply, it is possible to adjust the motor speed by adjusting the voltage frequency. This study was conducted to determine the effect of variable frequency
Get a quote
Variable Frequency Operation of Induction Motors
We will see in this chapter that all the good features of the mains operated induction motor are retained and all the bad characteristics detailed above can be avoided when the
Get a quote
Optimal frequency modulation of carrier waves and its application
Induction drive systems are widely used due to their low cost, long-term operational capability, and high reliability. These AC motors typically rely on inverters to
Get a quote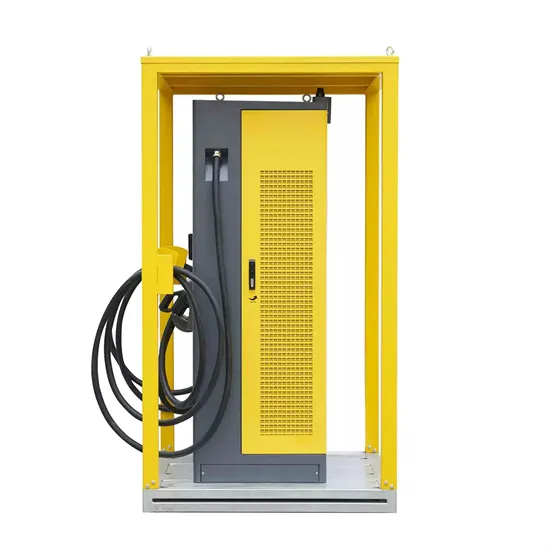
Fundamentals of Inverter–Fed Motors
New IGBT, PWM inverters can output very high switching frequencies, very rapid changes in voltage, and transient voltage spikes that can burn pin holes in the motors insulation causing
Get a quote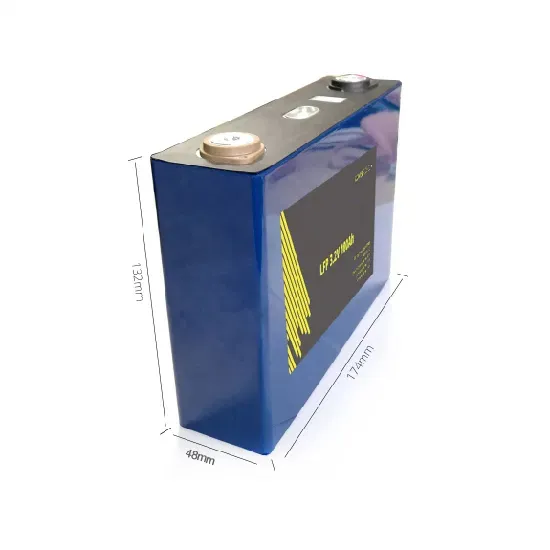
Analysis of the Asynchronous Motor Controlled by Frequency
In this sense, this article aims to determine the operational behavior of asynchronous motor controlled by frequency inverter applied in a fatigue test system for analysis of standardized
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [High frequency inverter induction motor rotation]
Does a variable speed drive inverter affect a three-phase induction motor?
With a variable speed drive inverter supply, it is possible to adjust the motor speed by adjusting the voltage frequency. This study was conducted to determine the effect of variable frequency by using a variable speed drive inverter on the performance of a three-phase induction motor.
What is a frequency inverter?
6 VI. Key Considerations When Using Frequency Inverters Frequency inverters, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), are essential components in modern motor control systems. These devices convert fixed-frequency AC power into variable-frequency power, allowing for precise control over motor speed, torque, and efficiency.
How do inverters get higher modulation frequency?
To get higher modulation frequency, each pulse must be very short and the inverter output goes from 0 volts to 650 volts DC in one–millionth of a second. This can seriously stress the motor’s insulation system. This is what the motor sees as the voltage pulse from a PWM output enters the motor windings.
Which type of inverter is used to control electric motors?
They are used in a number of applications both in industry and everyday life. There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical engineering. These can also be known as AC drives, variable speed drives (VSD), and variable frequency drives (VFD).
How does an inverter affect the speed of an AC motor?
The use of an inverter to adjust the speed and acceleration of an AC motor increases the range of applications of the motor compared with a motor that operates at a constant speed. The speed of a motor is normally measured as the number of revolutions per minute (rpm).
Can a frequency inverter run a motor above 50Hz?
While most motors are designed to operate at a frequency of 50Hz, there are many situations where higher speeds are necessary. Frequency inverters provide the flexibility to run motors above 50Hz, allowing for increased operational speeds and improved performance in certain applications.
Guess what you want to know
-
 High frequency inverter continuously turned on
High frequency inverter continuously turned on
-
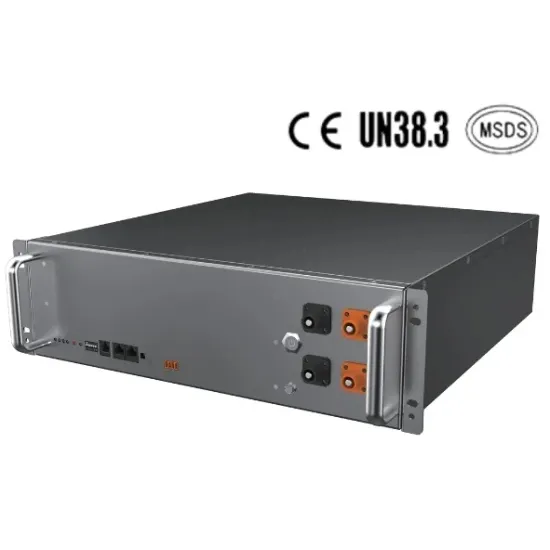
 High frequency inverter manufacturer
High frequency inverter manufacturer
-
 Yemen Huijue high frequency inverter manufacturer
Yemen Huijue high frequency inverter manufacturer
-
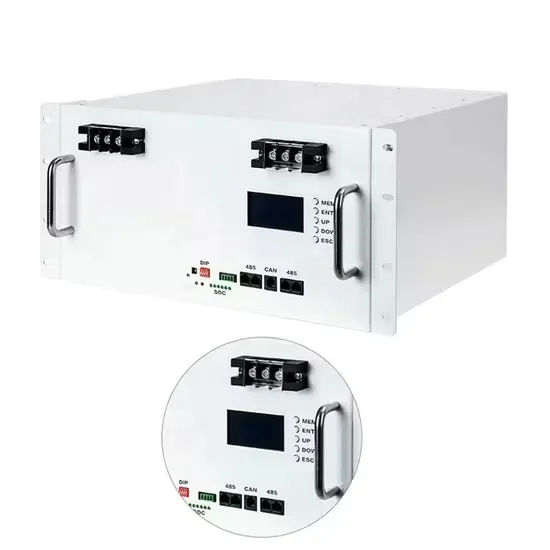
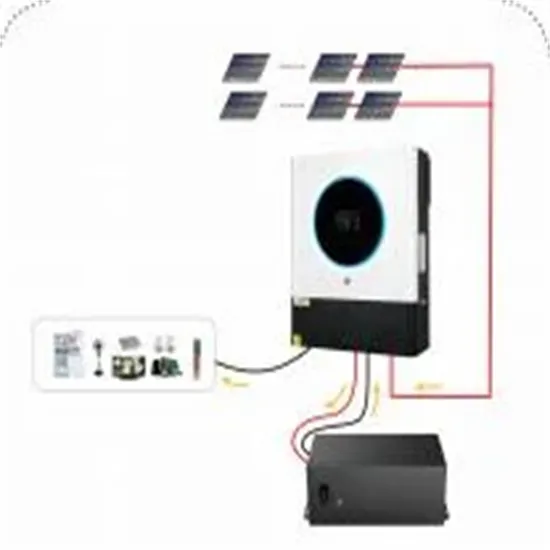 Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of dual silicon high frequency inverter
Advantages and disadvantages of dual silicon high frequency inverter
-
 German high frequency inverter price
German high frequency inverter price
-
 Simple sinusoidal high frequency inverter design
Simple sinusoidal high frequency inverter design
-
 Georgia High Frequency Inverter Device Factory
Georgia High Frequency Inverter Device Factory
-
 300KW high frequency inverter
300KW high frequency inverter
-
 High frequency inverter produces 1200v
High frequency inverter produces 1200v
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


