Subpart N—Operating Requirements
The subpart prescribes general oper-ating requirements for stations li-censed under this part. This includes station operating procedures, points of communication, permissible commu-nications,
Get a quote
1BY ORDER OF THE AIR FORCE MANUAL 17-2101
This Air Force Manual defines Air Force (AF) Long-Haul Communications (LHC) and assigns responsibilities for standardization and management of Long Haul Communications in the AF.
Get a quote
DHSUD eases guidelines on ICT infrastructure permits
In its Department Order (DO) No. 2020-009 or the Revised Locational Guidelines for Base Stations and Other Infrastructure for Cellular
Get a quote
Compliance Level of Base Transmission Stations with
Compliance Level of Base Transmission Stations with National Environmental Standards for Telecommunications and Broadcast Facilities in Calabar Metropolis, Southern Nigeria Inah
Get a quote
Army Facilities Management
The facilities engineer or user will furnish the initial purchase and installation of fire extinguishers in newly constructed facilities and their replacement in existing facilities, per NFPA 101, Life
Get a quote
Chapter 18.207 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FACILITIES
"Wireless communication facility" or "wireless facility" means the collective or combined equipment, network components or eligible support structures that are necessary or integral in
Get a quote
COMMUNICATION SITE BUILDING DESIGN AND
This chapter provides requirements and recommendations for designing communications site buildings, including equipment shelters and outdoor cabinets. The following topics are discussed:
Get a quote
Construction Requirements by Service
Construct and place into operation within 12 months of initial license grant date, or if modified under the Second Report and Order (FCC 96-27) on or before
Get a quote
47 U.S. Code § 1455
Notwithstanding section 704 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 (Public Law 104–104) or any other provision of law, a State or local government may not deny, and shall
Get a quote
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless
Get a quote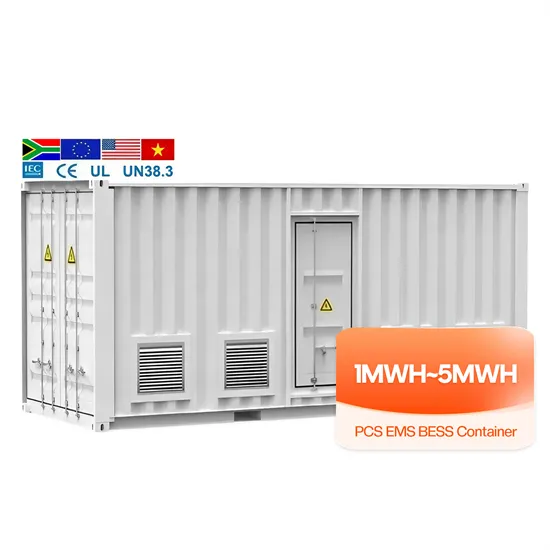
NASA FACILITIES DESIGN STANDARD
This NASA Technical Standard is approved for use by NASA Headquarters and NASA Centers and Facilities, and applicable technical requirements may be cited in contract,
Get a quote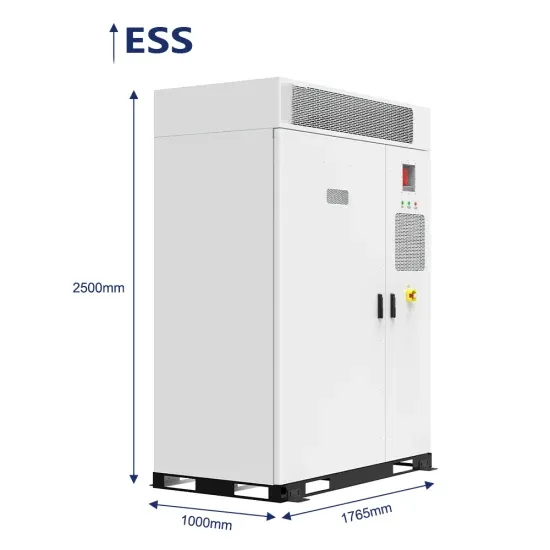
Proposed FCC Rules Could Limit NJ Municipalities''
The FCC proposes to clarify and implement the requirements of Section 6409 (a) of the Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012
Get a quote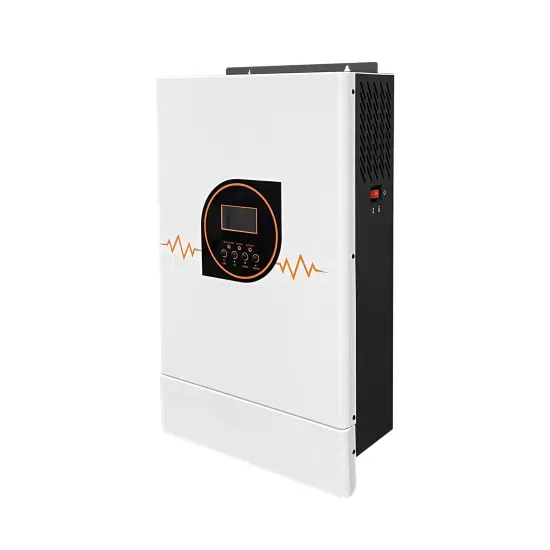
Base Stations
Base stations form a key part of modern wireless communication networks because they offer some crucial advantages, such as wide coverage, continuous communications and
Get a quote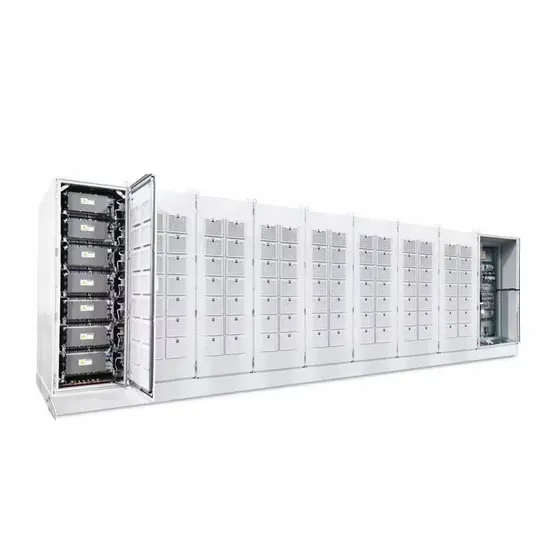
47 CFR Part 80 Subpart C -
(a) Each public coast station must exchange radio communications with any ship or aircraft station at sea; and each station on shipboard or aircraft at sea must exchange radio communications
Get a quote
Wireless Communications Facilities Design Guidelines
The definition of "base station" does not include any structure that, at the time the application is filed with the Town under Section 16A-3-250, Wireless Communication Facilities, does not
Get a quote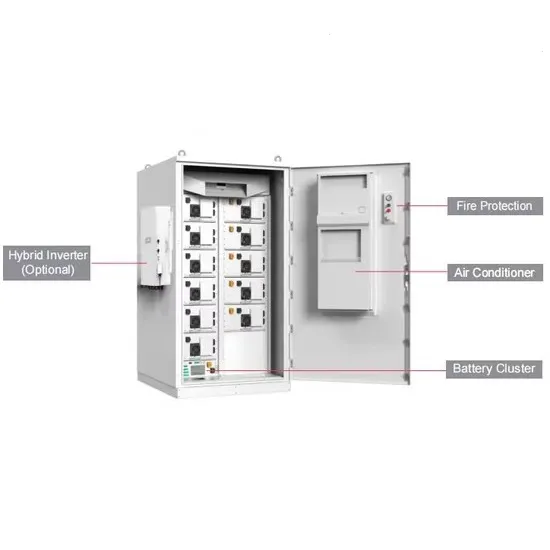
Construction Requirements by Service
Construct and place into operation within 12 months of initial license grant date, or if modified under the Second Report and Order (FCC 96-27) on or before August 15, 1996, or if base
Get a quote
DHSUD updates guidelines on ICT infra permits
The requirements and procedures in securing clearance for base stations and other telecommunication infrastructure were updated under the
Get a quote
Communications Facility. FAC: 1311
planning and preparation are key. Organizations developing requirements for new facilities should request pre-technical assistance from the supporting engineering and. installation Command
Get a quote
UFC 3-501-01 Electrical Engineering
Design buildings and similar support structures such as piers, wharfs, parking structures, sewage pump stations, and fueling facilities in accordance with the general requirements of NFPA 70:
Get a quote
eCFR :: 47 CFR Part 90 Subpart N -
This includes station operating procedures, points of communication, permissible communications, methods of station identification, control requirements, and station record
Get a quote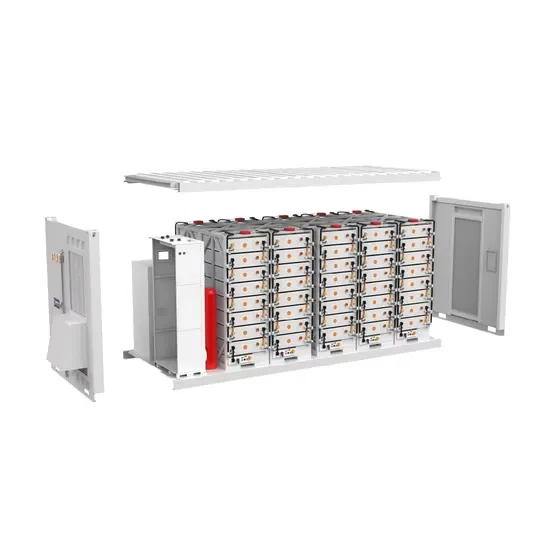
Reliability prediction and evaluation of communication base
In order to grasp the operation condition of post-earthquake communication base stations, Liu et al.1 from China Earthquake Administration conducted a study and analysis of typical seismic
Get a quote
Wireless Communication Facilities (WCF) Base Station or
Wireless Communication Facilities (WCF) Base Station or Alternative Tower Structure Review Procedure & Checklist The purpose of this guide is to provide general information about the
Get a quote
City of Bellevue Submittal Requirements
Proposed modification to a tower or base station meets at least one of the three threshold criteria below for an eligible facilities request. Check all that apply. Collocation of new transmission
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Requirements for base stations of communication facilities]
Why are base stations important in cellular communication?
Base stations are important in the cellular communication as it facilitate seamless communication between mobile devices and the network communication. The demand for efficient data transmission are increased as we are advancing towards new technologies such as 5G and other data intensive applications.
What are the rules governing the use of radio stations?
§ 80.86 International regulations applicable. In addition to being regulated by these rules, the use and operation of stations subject to this part are governed by the Radio Regulations and the radio provisions of all other international agreements in force to which the United States is a party. § 80.87 Cooperative use of frequency assignments.
What are the requirements for a radio station inspection?
§ 80.61 Commission inspection of stations. All stations and required station records must be made available for inspection by authorized representatives of the Commission. § 80.63 Maintenance of transmitter power. ( a) The power of each radio transmitter must not be more than that necessary to carry on the service for which the station is licensed.
What are the components of a base station?
Power Supply: The power source provides the electrical energy to base station elements. It often features auxiliary power supply mechanisms that guarantee operation in case of lost or interrupted electricity, during blackouts. Baseband Processor: The baseband processor is responsible for the processing of the digital signals.
What are the different types of base stations?
Some basic types of base stations are as follows: Macro-base stations are tall towers ranging from 50 to 200 feet in height, placed at strategic locations to provide maximum coverage in a given area. Those are equipped with large towers and antennas that transmit and receive radio signals from wireless devices.
What are the telephony requirements for a ship station?
Hand-held portable transmitters must be capable of reducing power to one watt, but need not do so automatically. § 80.81 Antenna requirements for ship stations. All telephony emissions of a ship station or a marine utility station on board ship within the frequency band 30-200 MHz must be vertically polarized.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Battery capacity requirements for communication base stations
Battery capacity requirements for communication base stations
-
 Business requirements for 2MWH energy storage system for communication base stations
Business requirements for 2MWH energy storage system for communication base stations
-
 Installation of flow battery equipment for indoor communication base stations
Installation of flow battery equipment for indoor communication base stations
-
 Battery layout of communication base stations
Battery layout of communication base stations
-
 Power supply costs for communication base stations
Power supply costs for communication base stations
-
 Are there base stations selling communication equipment in North Asia
Are there base stations selling communication equipment in North Asia
-
 What brands are there for wind and solar hybrid communication base stations
What brands are there for wind and solar hybrid communication base stations
-
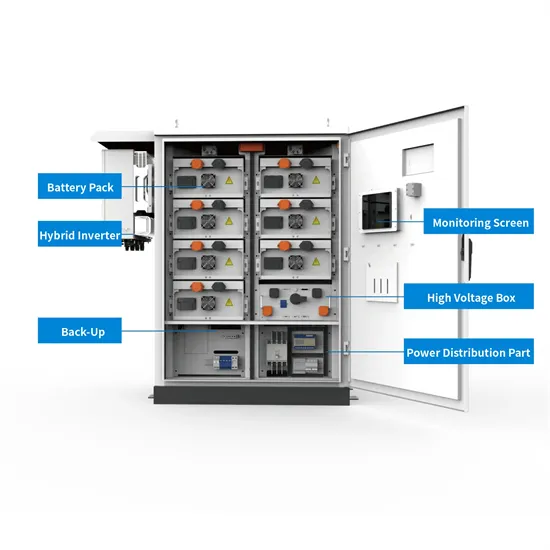 The cost of wind and solar complementary technology for Ecuadorian communication base stations
The cost of wind and solar complementary technology for Ecuadorian communication base stations
-
 The impact of wind power from communication base stations on house energy storage
The impact of wind power from communication base stations on house energy storage
-
 Comparison of wind power batteries for communication base stations
Comparison of wind power batteries for communication base stations
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


