How Discharging a Battery Affects Its Performance
Discharging a battery significantly impacts its performance and lifespan. Understanding how this process works is crucial for maximizing the
Get a quote
A Guide to Understanding Battery Specifications
Energy or Nominal Energy (Wh (for a specific C-rate)) – The "energy capacity" of the battery, the total Watt-hours available when the battery is discharged at a certain discharge current
Get a quote
What is Efficiency of Battery: Essential Insights for
The way a battery is used and charged also affects its aging process. Charge and Discharge Rates: Fast charging or discharging
Get a quote
Battery Terminology: Charge and Discharge of a Battery
Charging replenishes the energy depleted during discharge, preparing the battery for subsequent use. Discharge: In contrast, discharge occurs when the stored energy in the
Get a quote
Charge Flow Out of the Battery: Understanding Current,
During battery discharge, current flows from the positive electrode to the negative electrode. This flow happens because of a potential difference. The battery converts stored
Get a quote
Battery Charge And Discharge: 8 Powerful Insights To Maximize
Battery charge and discharge refer to the fundamental processes that allow a battery to store and release energy. Charging a battery involves applying an external electric
Get a quote
BESS Energy Storage Specs: Performance, Efficiency
2C Rate: The battery discharges in 30 minutes (e.g., 100 kWh battery discharges at 200 kW). Key Consideration: Select a C-rate that aligns with your
Get a quote
Full analysis of the battery charge and discharge rate
The charge and discharge rate of energy storage batteries refers to the ability of the battery to charge or discharge electricity within a certain
Get a quote
Charging and Discharging: A Deep Dive into the
As the battery charges, the voltage increases, and the battery''s state of charge (SoC) rises, indicating how much energy is stored. Modern
Get a quote
How do energy storage batteries discharge? | NenPower
Discharge cycles occur when the battery provides electrical energy to an external load. During this phase, the reverse of the charging process takes place; ions move back from
Get a quote
Lithium Battery Self-Discharge: Causes, Effects & Prevention Tips
Learn why lithium batteries lose charge over time, the factors affecting self-discharge, and how to minimize energy loss.
Get a quote
Charging and Discharging: A Deep Dive into the Working
As the battery charges, the voltage increases, and the battery''s state of charge (SoC) rises, indicating how much energy is stored. Modern battery management systems
Get a quote
Energy Storage Element Discharge Process: The Science Behind
Imagine your battery as a caffeinated squirrel storing nuts. The discharge process is basically that squirrel strategically dropping acorns (energy) where we need them. Here''s
Get a quote
Battery Energy Storage
In general, battery storage technology has high energy density, lower power density, and lesser cycle life. Batteries are suitable for applications that require long continuous discharge.
Get a quote
Basics of BESS (Battery Energy Storage System
Basic Terms in Energy Storage Cycles: Each number of charge and discharge operation C Rate: Speed or time taken for charge or discharge, faster means more power. SoC: State of Charge,
Get a quote
What are the charging and discharging cycles of a battery storage
In simpler terms, when you use an external power source, such as solar panels or the grid, to store energy in the battery, it is the charging phase. Conversely, when the stored
Get a quote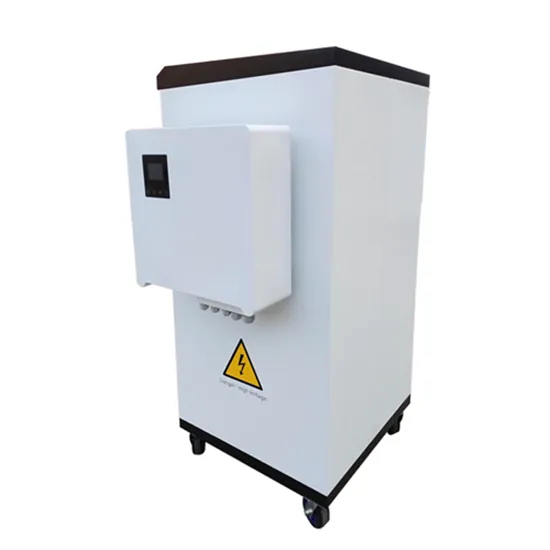
Why Does My Solar Battery Discharge to the Grid and How to
Key Takeaways Insufficient Storage Capacity: Limited battery capacity can lead to energy overflow, causing your solar battery to discharge excess energy back to the grid. High
Get a quote
How do batteries store and discharge electricity?
Assuming the battery has acquired its charged condition either by recharging or manufacturing, the aggregate effect of the chemical reactions taking place between the anode
Get a quote
Charging and discharging principles of lithium-ion
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices commonly used in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable
Get a quote
How Lithium-ion Batteries Work | Department of Energy
Lithium-ion batteries power the lives of millions of people each day. From laptops and cell phones to hybrids and electric cars, this technology is growing in popularity due to its
Get a quote
How Do Batteries Charge and Discharge? A Step-by-Step Guide
Discharging a battery is the opposite of charging. It occurs when the stored chemical energy is converted back into electrical energy, allowing the battery to power devices.
Get a quote
How do energy storage batteries discharge? | NenPower
Discharge cycles occur when the battery provides electrical energy to an external load. During this phase, the reverse of the charging process
Get a quote
Battery Terminology: Charge and Discharge of a Battery
Charging replenishes the energy depleted during discharge, preparing the battery for subsequent use. Discharge: In contrast, discharge
Get a quote
Why Depth of Discharge is Critical in Selecting an Energy Storage
Depth of Discharge refers to the percentage of a battery''s total capacity that can be used before recharging. It is essentially the inverse of another important energy storage
Get a quote
What is battery charging and discharging?-battery-knowledge
Charging and discharging are two fundamental processes that occur in batteries, and they serve opposite purposes. Here''s a breakdown of the key differences between these
Get a quote
Battery Energy Storage Systems: Main Considerations for Safe
This webpage includes information from first responder and industry guidance as well as background information on battery energy storage systems (challenges & fires), BESS
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Energy storage discharges when charging the battery]
What is the difference between charging and discharge of a battery?
Charging replenishes the energy depleted during discharge, preparing the battery for subsequent use. Discharge: In contrast, discharge occurs when the stored energy in the battery is released to power external devices or systems.
How does a battery charge work?
This process involves transferring electrons from the positive electrode (cathode) to the negative electrode (anode), creating a potential difference or voltage across the battery terminals. Charging replenishes the energy depleted during discharge, preparing the battery for subsequent use.
What happens when a battery is recharged?
Assuming the battery has acquired its charged condition either by recharging or manufacturing, the aggregate effect of the chemical reactions taking place between the anode and the cathode discharges electricity.
How do energy storage batteries work?
At their core, energy storage batteries convert electrical energy into chemical energy during the charging process and reverse the process during discharging. This cycle of storing and releasing energy is what makes these batteries indispensable for applications ranging from electric vehicles to grid energy management.
What happens when a battery is charged?
Let's go. Charge: When a battery is charged, electrical energy is stored within it through chemical reactions. This process involves transferring electrons from the positive electrode (cathode) to the negative electrode (anode), creating a potential difference or voltage across the battery terminals.
What happens when a lithium battery is discharged?
Energy Release: During discharging, lithium ions move back from the anode to the cathode. This movement generates an electric current that can be harnessed to power devices, vehicles, or feed electricity back into the grid. Voltage Drop: As the battery discharges, the voltage decreases, and the SoC drops.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Charging pile battery cascade utilization energy storage
Charging pile battery cascade utilization energy storage
-
 Battery with fast charging and large energy storage
Battery with fast charging and large energy storage
-
 Is the energy storage cabinet charging station available Battery price
Is the energy storage cabinet charging station available Battery price
-
 Energy storage cabinet station charging battery station cabinet
Energy storage cabinet station charging battery station cabinet
-
 Energy storage lithium battery fast charging
Energy storage lithium battery fast charging
-
 Energy storage charging pile energy storage cabinet battery cost price
Energy storage charging pile energy storage cabinet battery cost price
-
 Home energy storage fast charging lithium battery
Home energy storage fast charging lithium battery
-
 New Energy Storage Charging Pile Battery
New Energy Storage Charging Pile Battery
-
 Charging energy storage battery customization
Charging energy storage battery customization
-
 Energy storage cabinet outdoor battery cabinet solar charging panel 100w
Energy storage cabinet outdoor battery cabinet solar charging panel 100w
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


