Three-Phase Inverter Design | Tutorials on Electronics | Next
The most common three-phase inverter topology is the Voltage Source Inverter (VSI), where a fixed DC voltage is converted into a variable AC output. The VSI employs six power switches
Get a quote
Three Phase Multi-Level Inverter Topologies and
In this paper recently proposed three-phase multi-level inverter topologies and modulation techniques are discussed. Multilevel inverter topologies (MLIs) are more utilized in high
Get a quote
Comparison of AC/DC Power-Conversion Topologies for
Figure 12 shows the basic operation of a three-level T-type inverter, a bidirectional topology capable of both inverter and PFC modes. For a positive sine wave (VDC0 ≤ VAC ≤ VDC+), Q4
Get a quote
Multilevel Inverter Topology
Multilevel cascade inverters are used to eliminate the bulky transformer required in case of conventional multi-phase inverters, clamping diodes required in case of diode clamped
Get a quote
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working, Types & Its
A DC -to -AC converter which uses a DC power source to generate 3-phase AC power is known as a 3-phase inverter. This type of
Get a quote
A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
A concise summary of the control methods for single- and three-phase inverters has also been presented. In addition, various controllers applied to grid-tied inverter are thoroughly
Get a quote
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working and Its Applications
An inverter is a power electronic device, used to change the power from one form to other like DC to AC at the necessary frequency & voltage o/p. The classification of this can be done based
Get a quote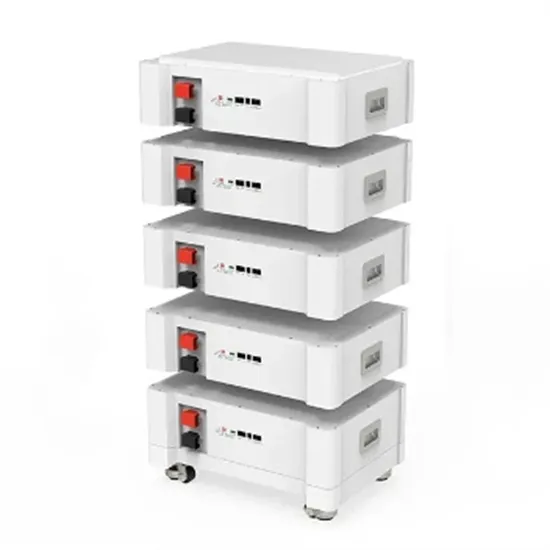
CHAPTER4
4.1 Introduction In this chapter the three-phase inverter and its functional operation are discussed. In order to realize the three-phase output from a circuit employing dc as the input voltage a
Get a quote
Three-Phase Inverter
The structure of a three-phase inverter is similar to a controllable three-phase rectifier, thus many inverters are bidirectional and can work in DC-AC inverter or AC-DC rectifier mode.
Get a quote
3-Phase Inverter
A three phase inverter is a device that converts dc source into three phase ac output . This conversion is achieved through a power semiconductor switching topology. in this
Get a quote
A technical review of modern traction inverter systems used in
The NPC MLI is a topology consisting of a series connection of diodes over a neutral point with controlled switches; Fig. 11 depicts the schematic representation of a 3-Φ
Get a quote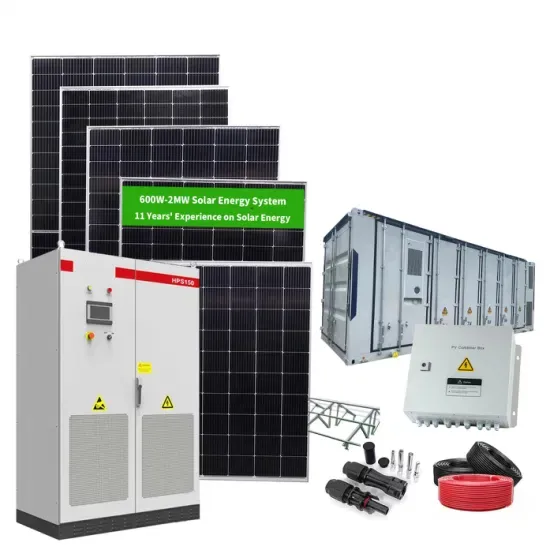
Three-Phase Inverters
Commonly the full-bridge topology is used for three-phase inverters. For three-phase applications including motor drives, UPSs, and grid-tied solar inverters, the three-phase full-bridge inverter
Get a quote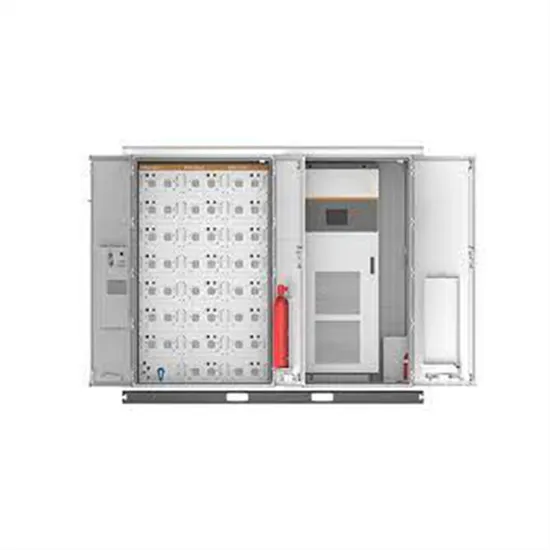
Three Phase Inverter | DC-TO-AC INVERTER
Here a critical load requiring 3-phase ac supply of fixed magnitude and frequency has been considered. In case ac mains supply fails, the 3-phase load may be electronically switched,
Get a quote
Overview of three-phase inverter topologies for distributed
The three-phase inverter topologies can be divided into three groups: the three-phase three-wire inverters, the three-phase four-wire inverters and the multilevel inverters.
Get a quote
Breaking Down the Shift: From 1/2-Phase to 3-Phase Modular Topology
System Design: What''s Changed? Traditional single/two-Phase Topology The traditional 75kVA Vertical system uses a 3-phase configuration built from three independent
Get a quote
Three-Phase Inverter Design | Tutorials on Electronics | Next
Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) The most common three-phase inverter topology is the Voltage Source Inverter (VSI), where a fixed DC voltage is converted into a variable AC output. The
Get a quote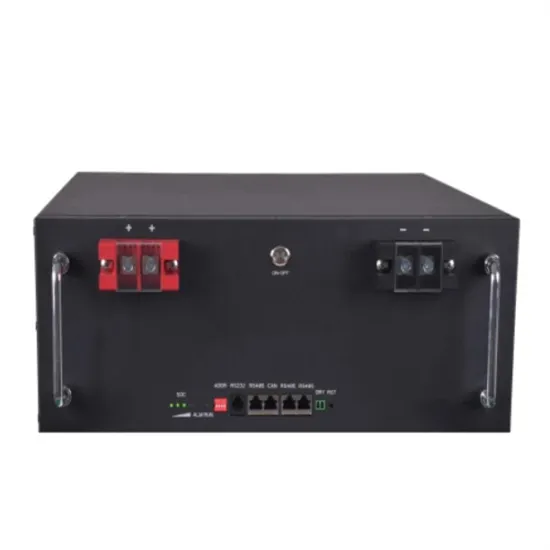
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working, Types & Its Uses
A DC -to -AC converter which uses a DC power source to generate 3-phase AC power is known as a 3-phase inverter. This type of inverter operates by using a power
Get a quote
(PDF) Overview of three-phase inverter topologies for
These topologies can be divided into three groups: the three-phase three-wire inverters, the three-phase four-wire inverters and the multilevel
Get a quote
A Comprehensive Review of Inverter Standards and
An inverter is a crucial component in grid-connected PV systems. This study focuses on inverter standards for grid-connected PV systems, as well as various inverter topologies for connecting
Get a quote
Microsoft Word
Example: An inverter with 700V DC-voltage (+/-350V) generates and 3 phase output signal with 400VAC phase to phase. The standard configuration with 3 halfbriges will switch the voltage
Get a quote
Three-Phase Inverter
The structure of the three-phase inverter is a simple extension of the full-bridge chopper using three half-bridges, as shown in Figure 2.9. It would be possible to create a converter using
Get a quote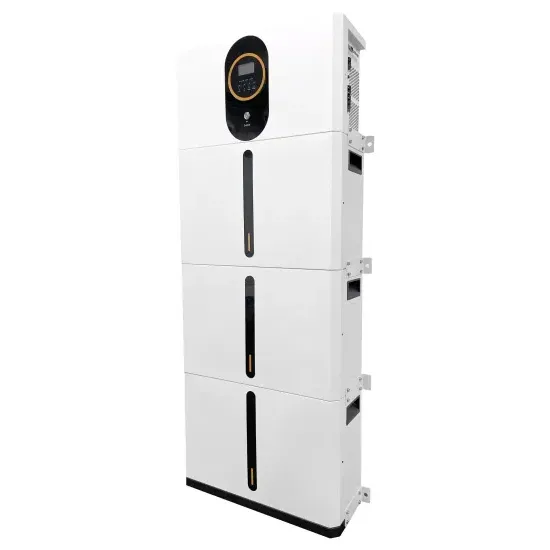
Comparison of different three phase inverter topologies: A review
This paper presents a comparative review of three different three phase inverter topologies namely the PWM Inverter, 180 Conduction Inverter, and the Multilevel Inverter.
Get a quote
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes, topologies and
The proliferation of solar power plants has begun to have an impact on utility grid operation, stability, and security. As a result, several governments have developed additional
Get a quote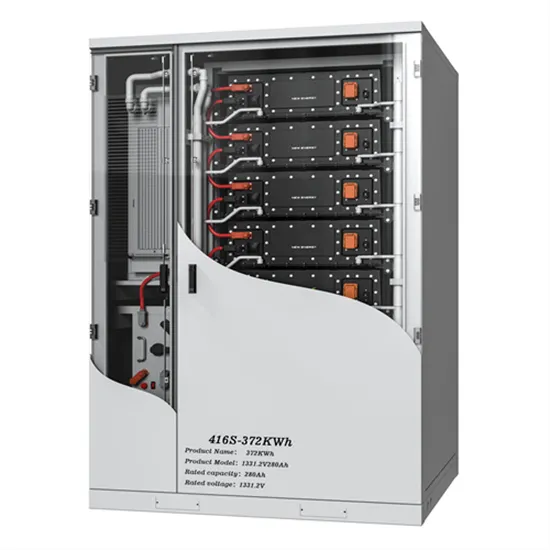
6 FAQs about [What topology does a three-phase inverter use ]
What are the applications of 3 phase inverter?
The applications of three phase inverter include the following. A three-phase inverter is mainly used for converting a DC input into an AC output. This inverter generates 3-phase AC power using a DC power source. It is used in high-power-based applications like HVDC power transmission.
What are the three-phase inverter topologies?
The three-phase inverter topologies can be divided into three groups: the three-phase three-wire inverters, the three-phase four-wire inverters and the multilevel inverters. In this paper, an overview of the aforementioned topologies is given.
What is a 3-phase inverter?
A DC -to -AC converter which uses a DC power source to generate 3-phase AC power is known as a 3-phase inverter. This type of inverter operates by using a power semiconductor switching topology.
Which topology is optimized for a three-level T-type inverter?
This topology is optimized even when selecting the same power switches. For a three-level T-type inverter with a power rating of 11 kVA, we selected SiC devices with an RDS(on) of 75 mΩ and a blocking voltage of 1.2 kV for Q1 and Q2, and 60 mΩ and 650 V for Q3 and Q4 (see Figure 40).
What is the topology of a three-phase full-bridge inverter?
The architecture is Figure 19: The Topology of a Three-Phase Full Bridge Inverter The 120-degree conduction mode and the 180-degree conduction mode are the two fundamental operating modes for three-phase full-bridge inverters, respectively.
How many switching states are there in a 3 phase inverter?
For the six switches of a three-phase inverter, there are only eight possible switch combinations, i.e., eight different switching states.
Guess what you want to know
-
 What is the price of a three-phase inverter in Bulgaria
What is the price of a three-phase inverter in Bulgaria
-
 What kind of inverter should I use for 60v
What kind of inverter should I use for 60v
-
 What size inverter can I use with a 48v lithium battery
What size inverter can I use with a 48v lithium battery
-
 What size battery should I use with a power frequency inverter
What size battery should I use with a power frequency inverter
-
 What size inverter should I use for a 36v solar panel
What size inverter should I use for a 36v solar panel
-
 What size battery inverter to use
What size battery inverter to use
-
 What battery to use when connecting to the inverter
What battery to use when connecting to the inverter
-
 What is a three-phase energy storage inverter
What is a three-phase energy storage inverter
-
 What inverter does Huawei Smart PV use
What inverter does Huawei Smart PV use
-
 What size battery should I use with an 8600w inverter
What size battery should I use with an 8600w inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


