Inverters, Types and Voltages
Browse our recommended inverters for every type of setup—from low voltage off-grid systems to high voltage, grid-tied solutions. Each product is reviewed to ensure it meets
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter Application Scenarios and Usage...
For occasions like outdoor camping, road trips, or mobile offices, high-frequency inverters provide convenient 220V AC power for daily small appliances. Their lightweight and compact form
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverter Circuit
A high frequency inverter circuit is an electronic circuit that allows for the conversion of DC electricity into AC power with a high frequency, usually around 60 Hz or more.
Get a quote
How does a high
Now, the main difference between high - frequency and low - frequency inverters lies in how they handle the conversion process, and this difference has a bunch of implications
Get a quote
High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverter: Which Has Higher
The two are similar, but the readers have noticed that the maximum PV voltage input of the high-frequency inverter is much higher than the maximum PV voltage input of the
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
In a typical high-frequency design, the incoming DC voltage is first chopped by a high-frequency DC-DC converter. This stage uses fast-switching power semiconductors, such
Get a quote
Advanced power inverter topologies and modulation techniques for
Such drive systems are usually fed by semiconductor switch-based inverters, which, unlike balanced pure sine-wave AC sources, produce large-amplitude, high-frequency
Get a quote
High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverter: Which Has Higher MPPT PV Voltage?
The two are similar, but the readers have noticed that the maximum PV voltage input of the high-frequency inverter is much higher than the maximum PV voltage input of the
Get a quote
Solar Pro 2.3, April & May 2009
In either case, the inverter may not interconnect and export power until the inverter records the proper utility voltage and frequency for a period of 5 minutes. These protections eliminate the
Get a quote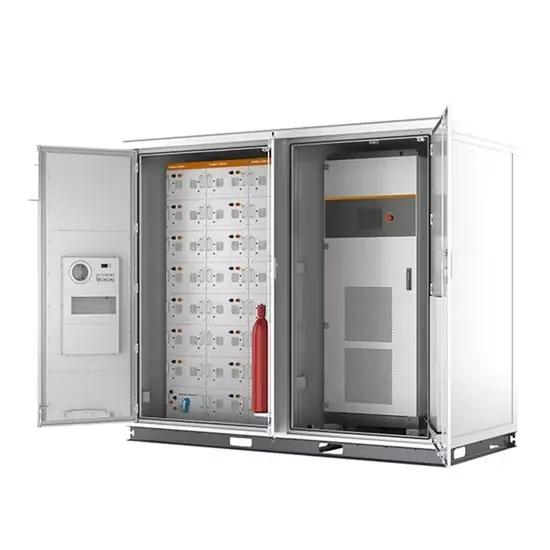
Advanced Inverter Functions to Support High Levels of
POLICY AND REGULATORY CONSIDERATIONS The use of advanced inverters in the design of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems can address some of the challenges to the integration of high
Get a quote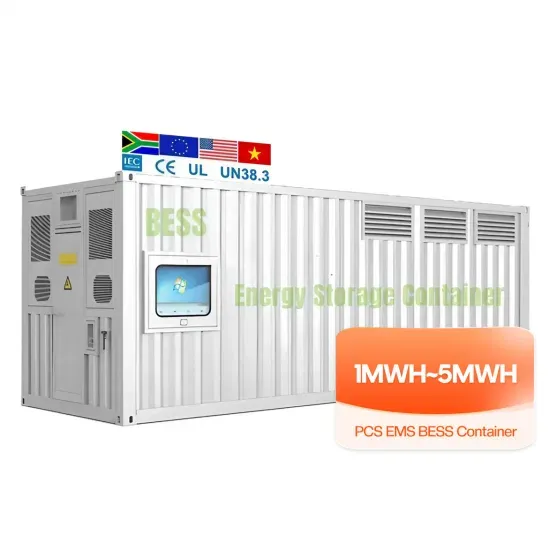
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which One Is Best?
A high-frequency inverter is a type of power inverter that uses advanced electronic switching technology to convert DC into AC. Instead of heavy transformers, these inverters use smaller,
Get a quote
A Very High Frequency dc-dc Converter Based on a Class
The resonant inverter accepts a dc input voltage, and generates very high frequency (VHF) ac, which is processed through the transformation stage to produce different ac voltage and
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High
In a typical high-frequency design, the incoming DC voltage is first chopped by a high-frequency DC-DC converter. This stage uses fast-switching power semiconductors, such
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
The use of high-frequency switching technology greatly improves the efficiency of high-frequency inverters, and their peak conversion efficiency
Get a quote
Troubleshooting Guide for Growatt Off Grid High Frequency
SPF 5000ES SPF 5000TL HVM WPV High Frequency inverter means that the frequency of mosfet swiching on and off is pretty high, in usual, it can reach 40KHZ.
Get a quote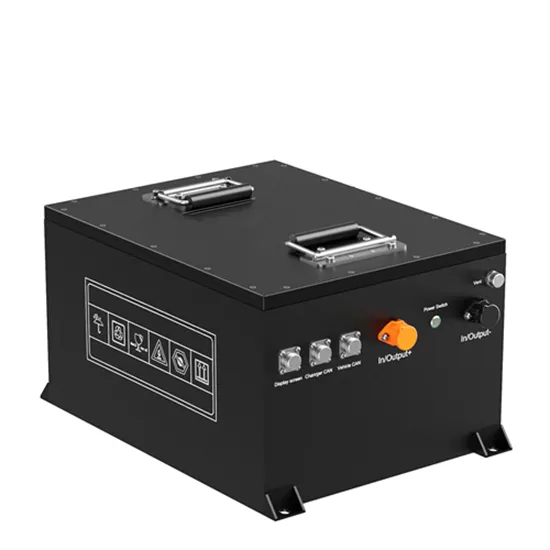
Inverters
Inverters Understanding Low Voltage vs. High Voltage Inverters and Low Frequency vs. High Frequency Inverters When setting up a solar energy system, choosing the right inverter is
Get a quote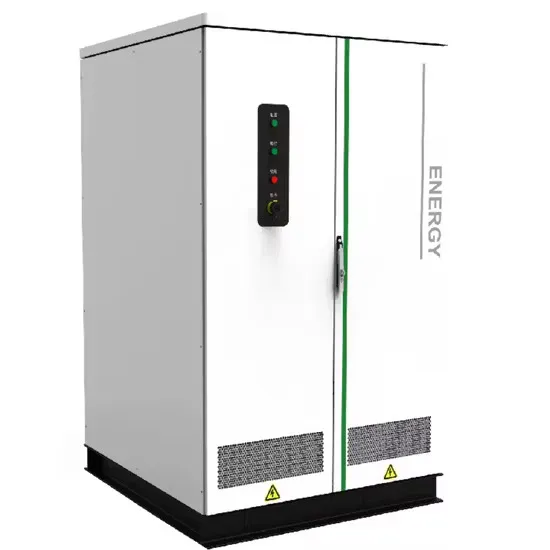
High Voltage Inverter Design
The main circuit includes an inverter DC power supply, IGBT bridge inverter, protection circuits, high frequency high voltage transformers, high frequency
Get a quote
How High Voltage Inverters Work
In many industrial applications, such as wind turbines, pumps and elevators, high voltage inverters are required to precisely control power. To summarize, a high voltage inverter is a
Get a quote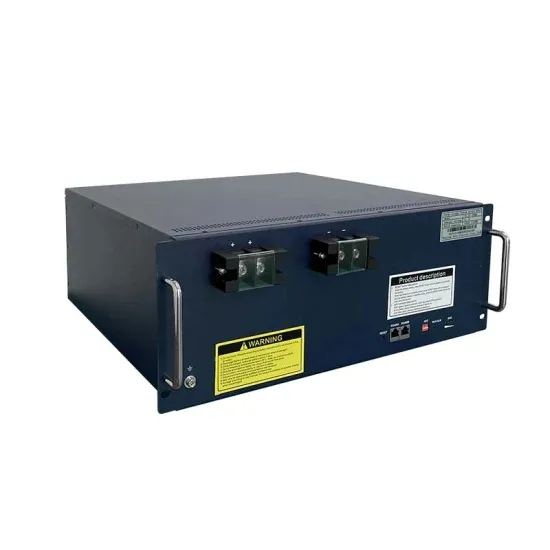
Overview of frequency control techniques in power
Power systems are rapidly transitioning towards having an increasing proportion of electricity from inverter-based resources (IBR) such
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
The use of high-frequency switching technology greatly improves the efficiency of high-frequency inverters, and their peak conversion efficiency can reach more than 90% in
Get a quote
Review on Silicon Carbide based High-Fundamental
ABSTRACT This article provides a comprehensive review of Silicon Carbide (SiC) based inverters designed for High-Speed (HS) drive applications, which require higher output frequencies to
Get a quote
Introduction to inverters: structure, operating
Inverter Features 1. High conversion efficiency and fast startup. Nowadays, with the development of technology, the energy conversion
Get a quote
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz.
Get a quote
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which
A high-frequency inverter is a type of power inverter that uses advanced electronic switching technology to convert DC into AC. Instead of
Get a quote
Low Frequency Vs. High Frequency Inverters
Aims uses low-frequency inverters, while most Growatt inverters are high-frequency, with some exceptions. If you''re unsure whether an inverter is low or
Get a quote
Microsoft Word
ABSTRACT This paper describes the analysis of the over voltage phenomena at the motor terminal of an inverter fed induction motor. The high frequency model for a three phase cable
Get a quote
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few
Get a quote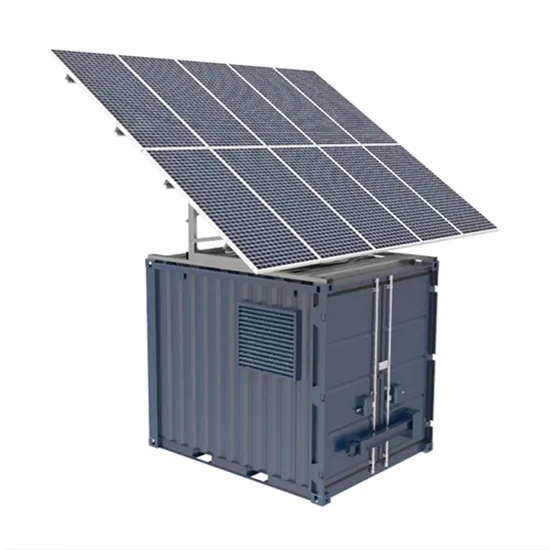
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inverter frequency, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and its practical implications.
Get a quote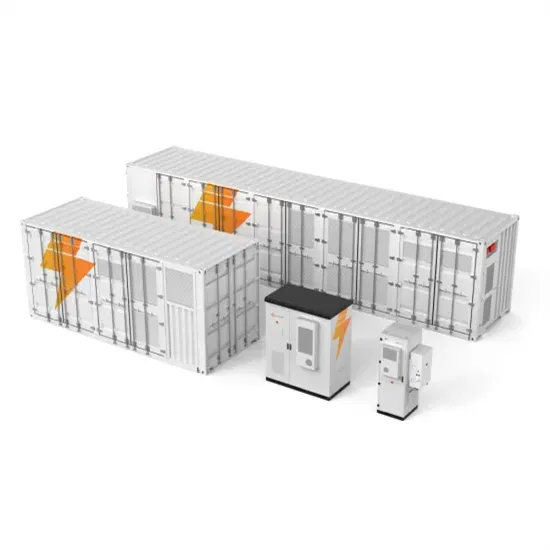
6 FAQs about [High frequency inverter voltage can reach]
What is a high frequency inverter?
A high-frequency inverter is a type of power inverter that uses advanced electronic switching technology to convert DC into AC. Instead of heavy transformers, these inverters use smaller, lightweight components that operate at very high switching speeds (several thousand Hz). High-frequency inverters are compact, lightweight, and efficient.
How do high frequency power inverters convert DC to AC?
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz. Low frequency inverter circuit diagram
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
Here is the major difference of them: Thanks to the heavy-duty transformer, low frequency inverters have much higher peak power capacity and reliability. The transformer handles higher power spikes with longer duration than high-frequency inverters when it comes to driving inductive loads such as electric motor, pump, compressor, air conditioners.
Should you buy a high-frequency inverter?
On the other hand, if you’re looking for a portable solution for RVs, boats, or small solar setups, a high-frequency inverter is ideal for powering lighter loads, such as laptops, LED lights, and small electronics.
What are the components of a high frequency inverter circuit?
The most important component of a high frequency inverter circuit is the transformer. This component is responsible for converting the DC current into AC power. Depending on the application, different types of transformers can be used, such as pulse width modulated (PWM), full wave, half wave, and peak-to-peak.
What is the maximum inverter frequency?
The maximum inverter frequency depends on its design specifications, with most commercial models offering a maximum frequency between 10 kilohertz to megahertz.
Guess what you want to know
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
-
 High voltage inverter 500w
High voltage inverter 500w
-
 Yemen Huijue high frequency inverter manufacturer
Yemen Huijue high frequency inverter manufacturer
-
 510 000 arc high voltage inverter high power
510 000 arc high voltage inverter high power
-
 Small high frequency inverter
Small high frequency inverter
-
 Use inverter when voltage is high
Use inverter when voltage is high
-
 Amorphous machine inverter high voltage
Amorphous machine inverter high voltage
-
 Spain high frequency inverter installation
Spain high frequency inverter installation
-
 Malaysia high frequency inverter price
Malaysia high frequency inverter price
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


